The Heat Island Effect
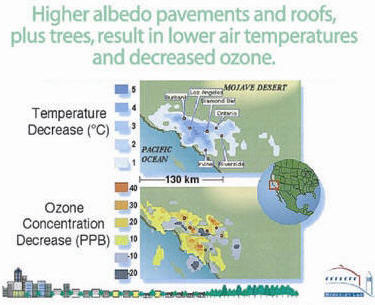 The heat island effect is a phenomenon which has accompanied and increased with urbanization, and it refers to the fact that man-made structures tend to attract and retain heat at a higher rate than is normal in nature. This results in an increase in ground-level ozone production by as much as 30%. In 2005, a tightly-packed urban area can average as much as twelve degrees warmer than its surrounding rural regions.
The heat island effect is a phenomenon which has accompanied and increased with urbanization, and it refers to the fact that man-made structures tend to attract and retain heat at a higher rate than is normal in nature. This results in an increase in ground-level ozone production by as much as 30%. In 2005, a tightly-packed urban area can average as much as twelve degrees warmer than its surrounding rural regions.
Choice of building material is key in reversing the heat island effect, for it is the dense, dark-colored structures which attract sunlight and retain it for long periods of time. Green rooftops, with their landscaping and incorporation of natural materials, are ideal in their resistance to heat absorption. The oxygen-releasing properties of trees and plants results in an even lower surface temperature.


